Marine Batteries: Starters, Deep Cycle, and Dual Purpose

Introduction
In the world of boating and marine adventures, a reliable and efficient power source is the backbone of any successful voyage. Marine batteries play a crucial role in providing electrical energy for a wide range of applications from starting engines to powering onboard electronics. In this blog post, we will explore the basics of marine batteries, and how to choose the right battery for your application.
What is a Marine Battery?
Marine batteries provide power for boats, yachts, and other watercrafts. They have three types based on their jobs: starting batteries, deep cycle batteries, and dual-purpose. The starting battery ensures reliable engine ignition, while the deep cycle battery provides a steady power supply for extended use of electrical systems and appliances on board. Dual-purpose marine batteries serve both starting and deep cycle purposes.

Starter Batteries
Marine starter batteries, also called marine cranking or engine start batteries, deliver high cranking and cold-cranking amps to start boat engines quickly.
Cranking amps is a measure of a battery’s ability to deliver a burst of power at 32°F (0°C) for 30 seconds while maintaining a minimum voltage. CA is commonly used to assess the battery’s starting power in relatively mild or moderate climates, where the temperatures are not extremely cold.
Cold Cranking Amps, on the other hand, are a more stringent measure of a battery’s starting power. It is defined as the maximum current a battery can deliver at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds while maintaining a minimum voltage. CCA is crucial for cold weather starting, where the engine oil may be thicker, making it more challenging for the engine to turn over. For more information on cold cranking amps check out our blog post, “What are CCAs”.

Deep Cycle Batteries
Deep-cycle marine batteries deliver steady, long-lasting power, making them ideal for continuous-use applications. Unlike starting batteries, they have thicker lead plates to handle repeated deep discharges and recharges without damage.
These batteries commonly power boat systems and appliances, including lights, trolling motors, fish finders, radios, and refrigerators. Deep-cycle marine batteries are crucial for boating activities that demand a reliable and long-lasting power source, ensuring that boaters can enjoy their time on the water without worrying about power interruptions.
Dual Purpose
Dual-purpose batteries aim to provide a balance between the characteristics of cranking (starting) batteries and deep-cycle batteries. These batteries deliver the high burst of power needed to start an engine while also being capable of providing a moderate amount of sustained power for running onboard electronics and accessories.
Many deep-cycle marine batteries on the market today have dual-purpose capability. If you have a smaller boat with a less demanding engine, a quality dual-purpose deep-cycle marine battery might be sufficient to start the engine and power accessories. For larger boats with powerful engines or many electronics, use a dedicated cranking battery for starting and a separate deep-cycle battery for accessories.

How are Marine Batteries Different?
Marine batteries have specific characteristics to withstand the unique challenges of the marine environment, such as constant motion, vibration, and exposure to moisture. They withstand vibrations and shocks on boats, especially in rough waters or at high speeds, thanks to reinforced construction and secured internal plates. Due to the potential risks associated with marine environments, marine batteries often have additional safety features. For example, some marine batteries are equipped with spark arrestors to prevent explosions in case of an accidental spark during charging.
Additionally, marine batteries resist corrosion caused by exposure to saltwater and other corrosive elements found in the marine environment. They typically use materials that are more resistant to corrosion, such as lead alloys. Lastly, marine batteries can come with different terminal types and sizes to accommodate various boat setups and electrical systems. For example, some marine batteries have specialized terminal designs to prevent accidental short circuits or to enable quick-connect features.

What Size Marine Battery Do I Need?
Marine batteries come in various sizes to accommodate different power requirements and fit specific battery compartments on boats. Marine battery size typically uses group numbers or letters to identify different sizes. Larger group sizes generally offer higher capacity and are suitable for applications with higher power demands, such as powering multiple electronics and accessories. Smaller group sizes are ideal for smaller boats or those with lower power requirements. Choosing the right marine battery size ensures optimal performance, efficient space utilization, and reliable power supply for various applications during boating adventures. You can learn more about marine battery sizing here.
Lithium or Lead Acid?
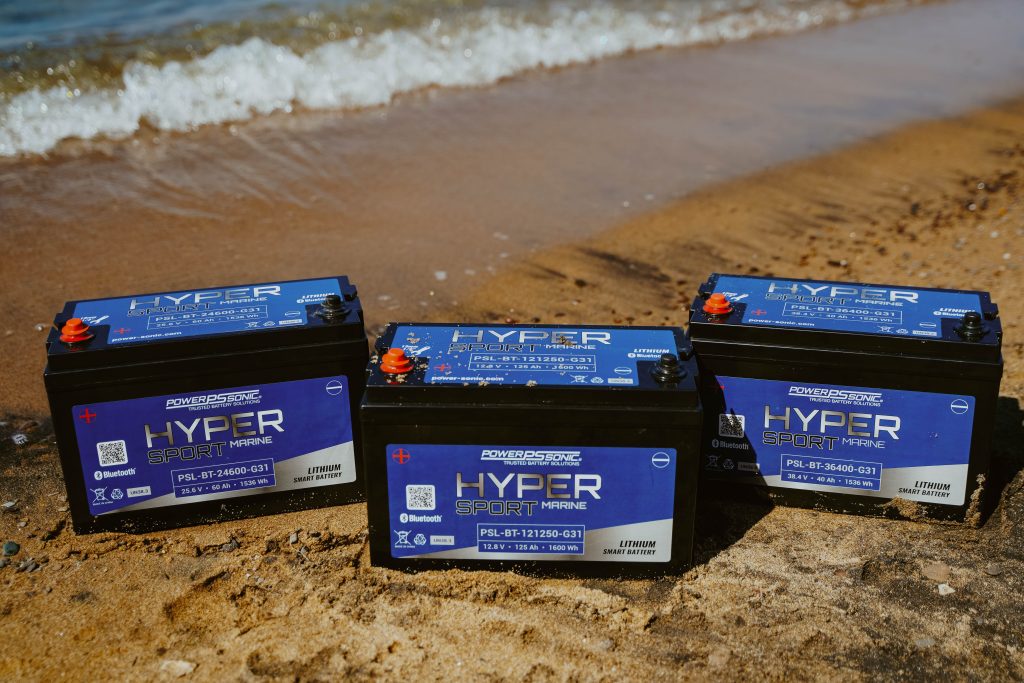

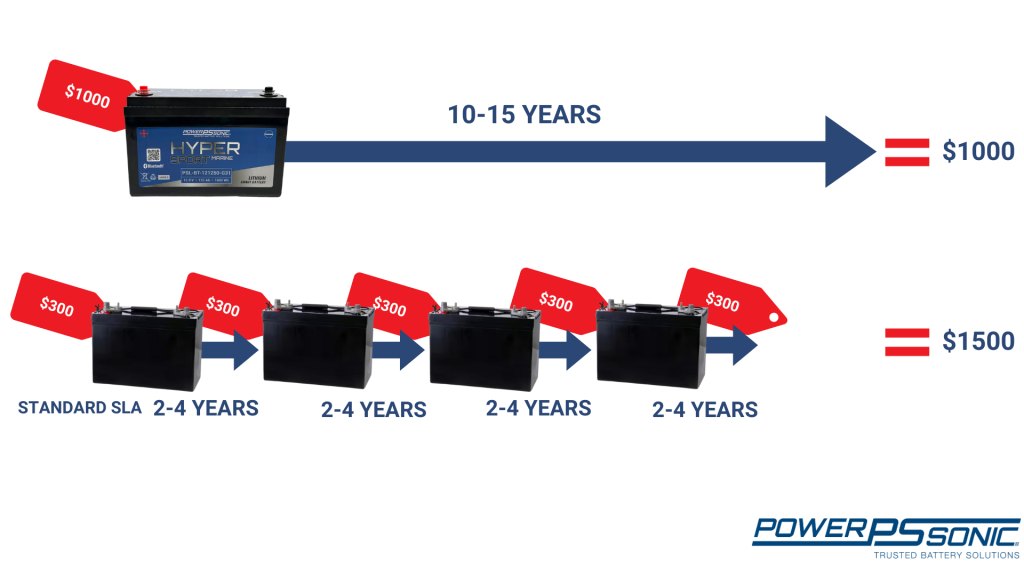
Lithium batteries offer a host of significant advantages that make them an excellent choice for marine applications. One of their key strengths lies in their exceptional energy density, allowing them to store more power in a smaller and lighter package compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. This weight reduction not only enhances boat performance but also optimizes fuel efficiency and handling. Another prominent advantage is their long cycle life, enduring thousands of charge and discharge cycles, far outlasting lead-acid batteries. This longevity ensures boaters can rely on lithium batteries for extended periods without frequent replacements, providing a more reliable power source for their marine adventures.
Additionally, lithium batteries charge more efficiently, reducing downtime and maximizing water time, and despite higher upfront costs, they offer long-term savings and efficiency.You can learn more about the benefits of lithium here.
While lithium batteries are considered the optimal choice for marine applications, lead-acid batteries offer their own set of advantages. They have a lower upfront cost, providing a budget-friendly option for boaters looking to power their vessels without breaking the bank. Another advantage is their safety and reliability. Lead-acid batteries have a proven track record in the marine industry and excel at starting applications because they lack over-current protections. Check out Battery Universities’ article, “Can the Lead-Acid Battery Compete in Modern Times?’ for more advantages of lead acid.
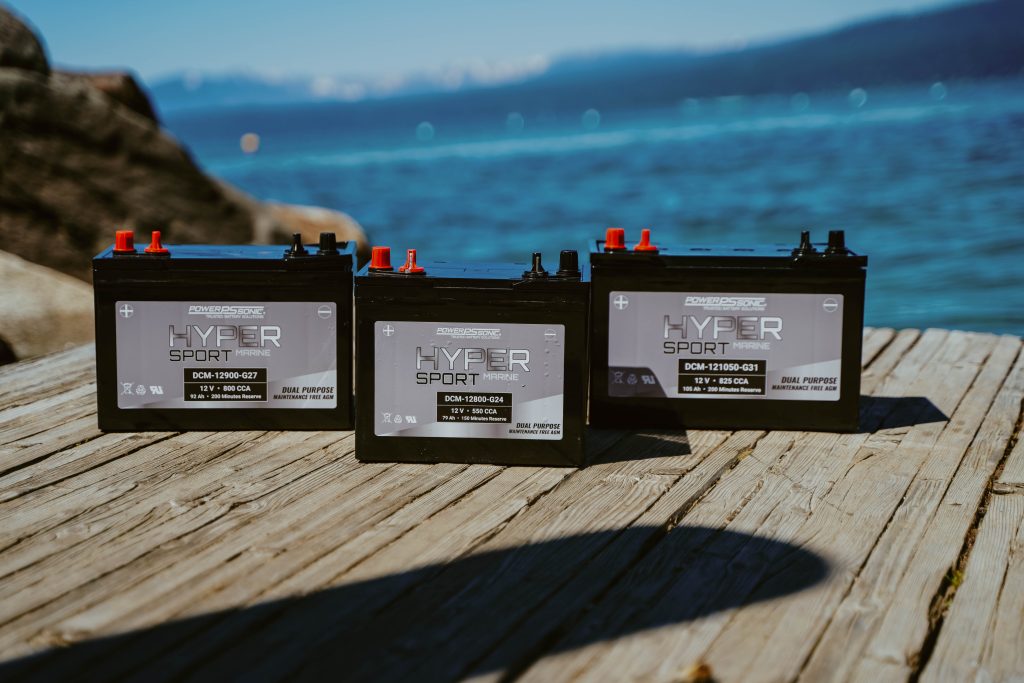

How Long Do Marine Batteries Last?
The lifespan of marine batteries varies depending on their type. Starting batteries, designed for quick bursts of high current, typically last around 3 to 5 years. Deep cycle batteries, engineered for sustained power delivery, can endure between 2 to 4 years when well-maintained. Lithium marine batteries, on the other hand, can last 10 to 15 years!
Frequent use and deep discharging can put additional stress on lead acid marine batteries, leading to faster wear and shorter lifespans. Properly managing discharge levels and avoiding over-discharging can significantly extend battery life. Additionally, correct charging practices are crucial for battery longevity. Overcharging or undercharging can harm marine batteries, reducing their service life. Using smart chargers and performing regular maintenance, like cleaning terminals and shielding batteries from extreme conditions, helps preserve battery health and extend lifespan.
How Should a Marine Battery Be Stored?
Choose a storage location that is cool, dry, and well-ventilated. Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight, as both can accelerate the battery’s degradation. A stable storage environment helps preserve the battery’s performance and protects it from unnecessary wear. Before storing the marine battery charge the battery according to the manufacturer’s recommendation. To learn more, check out Battery Universities’ article, “How to Store Batteries”.

Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the basics of marine batteries is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with your boating needs. Marine batteries are built with unique features to endure the harsh environment at sea. Both lithium and lead acid battery types have their advantages and considerations for marine applications. When choosing between the two, consider factors such as power requirements, available space, weight capacity, and budget constraints. Careful battery selection ensures that your marine adventures are powered efficiently and reliably, allowing you to embark on memorable journeys with peace of mind.



