kW vs kWh

Is kilowatt the same as kilowatt-hour? The quick answer is no. Although kilowatt (kW) and kilowatt-hour (kWh) are related, they are, in fact, completely different. Understanding kW vs kWh is crucial as they measure different aspects of electricity usage. In this guide, we will explain the difference, what they measure, and why it is important to understand the difference.
The Difference Between Kilowatt vs. Kilowatt-Hour
Kilowatts (kW) and kilowatt-hours (kWh) are related but measure different things: kW measures power—the rate of electricity use—while kWh measures energy—the total electricity used over time.
Time is key: kWh equals kW multiplied by hours. For example, charging an EV with a 22 kW charger for one hour consumes 22 kWh (22 kW × 1 hour = 22 kWh).
In the example below, a Level 2 charger (7.5 kW) and a Level 3 charger (60 kW) show power on the left and energy consumed over 2 hours on the right. Using the equation kW × hours = kWh, the Level 2 charger uses 15 kWh (7.5 kW × 2 hours).
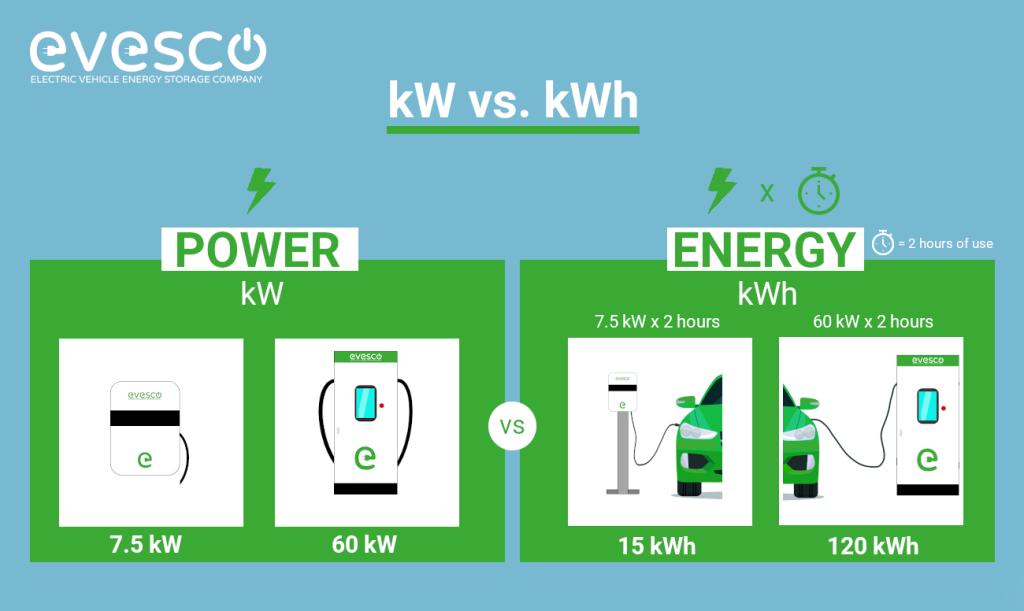
Let’s quickly summarize kW and kWh.
What is a kW (kilowatt)?
A kW or kilowatt is a unit of measurement for the rate of power an electrical device or load uses. The higher the kW of a device, the more electrical power is needed to operate it. A kilowatt is 1000 watts (W).
1000 W = 1 kW
What is a kWh (kilowatt-hour)?
A kWh or kilowatt-hour measures the energy usage of an electrical device or load. The higher the rate of power (kW) of an electrical device and the longer it is used (hours), the more electricity it consumes (kWh).
Let’s look at some examples of kW vs. kWh about both low and high-power electrical devices and see how they affect each other.
If you use a low-powered electrical device such as a 65-inch LED TV, which needs 100 watts (0.1 kW) of power, you can use it for ten hours before consuming 1 kWh of energy. On the other hand, if you are operating a 60 kW DC fast EV charger, you will consume 1 kWh of energy within one minute.
| Electrical Device | Power (kW) | Usage (hours) | Energy Consumed (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 65-inch LED TV | 0.1 | 10 | 1 |
| Air conditioning | 2.5 | 1.5 | 3.75 |
| Home EV charger | 3.5 | 10 | 35 |
| Level 2 EV charger | 22 | 8 | 176 |
| DC fast EV charger | 60 | 0.5 | 30 |
Why is it Important to Know the Difference Between kW and kWh?
Understanding the difference between kW and kWh is essential for any business looking to monitor and manage its electricity usage. It is also crucial for any business looking to introduce EV charging, as utility companies typically charge for energy consumption in kWh and peak power demand in kW. Knowing when and at what rate electricity is being consumed can enable businesses to reduce their overall electric bills.
kW and kWh in Relation to Electric Vehicles
When it comes to Electric Vehicles (EVs), it is essential to know the difference between kilowatts and kilowatt-hours. An EV stores the electricity to propel itself in a battery; this battery is sized in kWh. EVs have different battery capacities—for example, the Ford F-150 Lightning Pro has 98 kWh, while the BMW i4 eDrive35 has 70.2 kWh. Batteries are measured in kWh, but charging power is measured in kW. Higher kW chargers generally charge faster, but charging time also depends on the EV’s charging level, charge acceptance rate, and battery size.
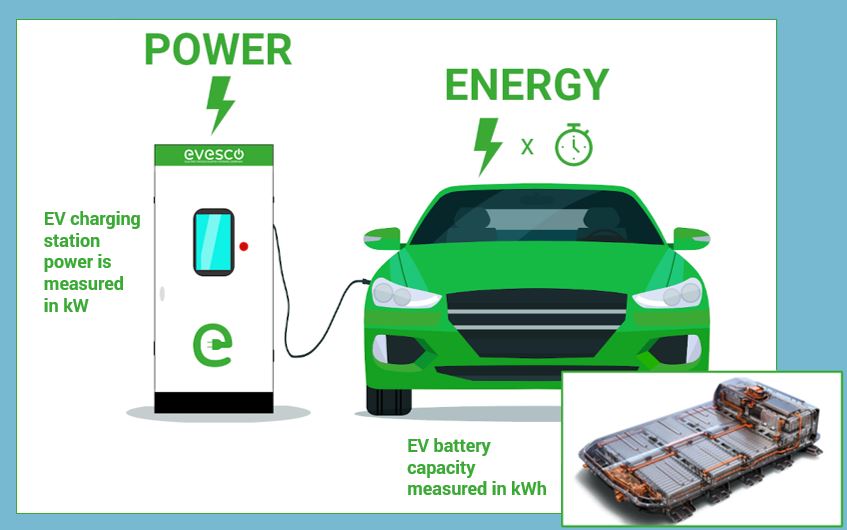
In short, kWh measures an EV battery’s capacity, while kW measures the charger’s power. Charger kW and usage time determine the energy delivered to the battery in kWh.



